Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS); Media formats and codecs
Multiple media elements shall be combined into a composite single MM using MIME multipart format. The media type of a single MM element shall be identified by its appropriate MIME type whereas the media format shall be indicated by its appropriate MIME subtype. In order to guarantee a minimum support and compatibility between multimedia messaging capable terminals, MMS User Agent supporting specific media types shall comply with the following selection of media formats:
Text
Plain text. Any character encoding (charset) that contains a subset of the logical characters in Unicode shall be used (e.g. US-ASCII, ISO-8859-1, UTF-8, Shift_JIS, etc.). Unrecognized subtypes of "text" shall be treated as subtype "plain" as long as the MIME implementation knows how to handle the charset. Any other unrecognized subtype and unrecognized charset shall be treated as "application/octet - stream".
Speech
The AMR codec shall be supported for narrow-band speech.
The AMR wideband speech codec shall be supported when wideband speech working at 16 kHz sampling frequency is supported.
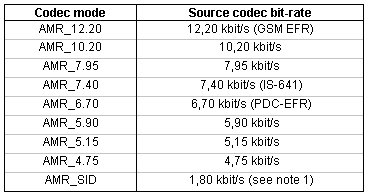 |
Source codec bit-rates for the AMR codec
Audio
MPEG-4 AAC Low Complexity object type should be supported. The maximum sampling rate to be supported by the decoder is 48 kHz. The channel configurations to be supported are mono (1/0) and stereo (2/0). In addition, the MPEG-4 AAC Long Term Prediction object type may be supported.
Synthetic audio
The Scalable Polyphony MIDI (SP-MIDI) content format defined in Scalable Polyphony MIDI Specification and the device requirements defined in Scalable Polyphony MIDI Device 5-to-24 Note Profile for 3GPP should be supported. SP-MIDI content is delivered in the structure specified in Standard MIDI Files 1.0, either in format 0 or format 1.
Still Image
ISO/IEC JPEG together with JFIF shall be supported. The support for ISO/IEC JPEG only apply to the following two modes:
| mandatory: baseline DCT, non-differential, Huffman coding
optional: progressive DCT, non-differential, Huffman coding
Bitmap graphics
The following bitmap graphics formats should be supported:
GIF87a
GIF89a
PNG
Video
For terminals supporting media type video, ITU-T Recommendation H.263 profile 0 level 10 shall be supported. This is the mandatory video codec for the MMS. In addition, MMS should support:
H.263 Profile 3 Level 10
MPEG-4 Visual Simple Profile Level 0
These two video codecs are optional to implement.
NOTE: ITU-T Recommendation H.263 baseline has been mandated to ensure that video-enabled MMS support a minimum baseline video capability and interoperability can be guaranteed (an H.263 baseline bitstream can be decoded by both H.263 and MPEG-4 decoders). It also provides a simple upgrade path for mandating more advanced codecs in the future (from both the ITU-T and ISO MPEG).
ITU press release regarding H.264 video compression standard (23/12/02)
Etsi and Digital Video Broadcasting Project are developing DVB-X standard for UMTS. Read the EETimes article. (11/10/03)
Vector graphics
For terminals supporting media type "2D vector graphics" the "Tiny" profile of the Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG-Tiny) format shall be supported, and the "Basic" profile of the Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG-Basic) format may be supported.
World Wide Web Consortium Issues Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) 1.1 and Mobile SVG as W3C Recommendations (14/01/03)
File format for dynamic media
The file format used in the present document for timed multimedia (such as video, associated audio and timed text) is structurally based on the MP4 file format. However, since non-ISO codecs are used here, it is called the 3GPP file format and has its own file extension and MIME type to distinguish these files from MPEG-4 files. When the present document refers to the MP4 file format, it is referring to its structure (ISO file format), not to its conformance definition.
To ensure interoperability for the transport of video and associated speech/audio and timed text in an MM, the MP4 file format shall be supported. The usage of the MP4 file format shall follow the technical specifications and the implementation guidelines specified in TS 26.234.
Media synchronization and presentation format
The mandatory format for media synchronization and scene description of multimedia messaging is SMIL.
The 3GPP MMS uses a subset of SMIL 2.0 as format of the scene description. MMS clients and servers with support for scene descriptions shall support the 3GPP PSS5 SMIL Language Profile. This profile is a subset of the SMIL 2.0 Language Profile but a superset of the SMIL 2.0 Basic Language Profile. TS 26.234 also includes an informative annex B that provides guidelines for SMIL content authors.
Additionally, 3GPP MMS should provide the following format:
XHTML Mobile Profile
The 3GPP MMS uses a subset of XHTML 1.1 as a format for scene description. MMS clients and servers with support for scene descriptions shall support XHTML Mobile Profile, defined by the WAP Forum. XHTML Mobile Profile is a subset of XHTML 1.1 but a superset of XHTML Basic. |





No comments:
Post a Comment